Addressing water quality challenges. Innovative solutions for municipalities and industries facing emerging contaminants
Municipalities and industries face rising water quality challenges as traditional treatment methods fail against contaminants like PFAS and heavy metals. Advanced solutions like Nanostone ceramic membranes ensure cleaner water, regulatory compliance, and operational efficiency for a sustainable future.
January 27, 2025

Water quality challenges are becoming a serious concern for both municipalities and industries that depend on reliable water sources. Traditional water treatment methods are increasingly insufficient as they fail to keep up with the rise of complex contaminants and the growing demands of modern industries. As these sectors face escalating pressure from both regulatory standards and the need for higher quality water, finding effective, cost-efficient solutions has never been more urgent.
The Pressure on Municipal Water Systems
Municipal water treatment plants are under significant strain, facing contaminants like PFAS, heavy metals, and endocrine-disrupting compounds (EDCs). These substances, while long present in various water sources, have become much harder to remove as traditional filtration systems fail to keep pace with the complex nature of modern pollution. PFAS, in particular, are notoriously difficult to filter out because they are persistent in the environment and resistant to degradation. When it comes to dealing with the health risks of these substances, municipalities are now tasked with finding solutions that meet stringent water quality standards.

Suspended solids and high Total Dissolved Solids (TDS) are also a growing problem. When high levels of suspended particles or dissolved solids are present, treatment plants face challenges in purifying water to a potable standard. This issue is exacerbated by extreme weather patterns, which have become more frequent due to climate change. Stormwater runoff from heavy rainfall can flush significant amounts of contaminants into surface water, further complicating treatment efforts. The increased turbidity from such events can overwhelm filtration systems, making it difficult for municipalities to maintain consistent water quality.
To meet regulatory compliance and maintain public health, municipalities need to modernize their water treatment technologies. The cost of retrofitting or replacing outdated systems can be substantial, and without the proper tools, many local water authorities are simply unable to cope with these rising challenges.
Industry-Specific Challenges
Industries that rely on high-quality water for production face equally pressing challenges. Water treatment is essential in sectors like power generation, food processing, and semiconductor manufacturing, where even trace amounts of contaminants can disrupt operations or product quality.
For power plants, water is crucial for cooling processes. When high levels of TDS or salts are present, these substances can form scales on heat exchangers, which reduces operational efficiency and leads to frequent maintenance shutdowns. If untreated, these contaminants can severely damage critical equipment, adding unnecessary costs to operations. The need for effective water treatment in these plants is not just a regulatory concern, but also a matter of operational reliability.In the semiconductor industry, the stakes are even higher. Water used in the production of microelectronics needs to be ultra-pure. Even small amounts of dissolved solids or organic compounds can ruin batches of chips, leading to costly defects. As the global demand for electronics grows, so does the pressure on industries to ensure that water used in manufacturing meets stringent purity standards. Any deviation can lead to serious losses.

Similarly, in the food processing and pharmaceutical sectors, contaminants like heavy metals or suspended solids can compromise product quality and safety. These industries are highly regulated, and any lapse in water quality can lead to health risks for consumers and significant legal consequences for manufacturers.
The Role of Emerging Technologies in Solving Water Quality Issues
Given these mounting challenges, it’s clear that traditional methods can no longer meet the needs of both municipalities and industries. However, newer technologies, such as ceramic membrane filtration solutions, are offering more effective alternatives.
Nanostone ceramic membranes, for instance, are increasingly being adopted by both municipalities and industries facing challenging water quality issues. These membranes are specifically designed to handle difficult-to-remove contaminants like PFAS, heavy metals, and suspended solids. Their ability to operate effectively under high pressures and resist fouling makes them an ideal solution for water treatment plants and industrial processes.
In municipal water treatment, ceramic membranes can provide reliable filtration during periods of high turbidity, such as during storms or algal blooms. Their durability and lower maintenance requirements allow plants to stay operational longer without requiring frequent system shutdowns or costly repairs.
For industries, these membranes can help ensure that water used in production processes meets the highest standards of purity. In sectors like semiconductors, where water purity is crucial for product integrity, ceramic membranes can deliver the level of filtration needed to remove even the smallest contaminants, thus preventing costly product defects.
A Growing Need for Advanced Filtration
As water quality challenges intensify, municipalities and industries must embrace innovative solutions to keep pace with the evolving landscape of contaminants and regulatory demands. Traditional treatment methods are no longer sufficient, and the need for advanced technologies has never been more critical. Ceramic membrane filtration offers a promising alternative, providing a reliable, cost-effective solution to tackle persistent contaminants like PFAS, heavy metals, and suspended solids. These systems are designed to withstand the complex conditions faced by both municipal water treatment plants and high-demand industries, ensuring efficient and sustainable water management.
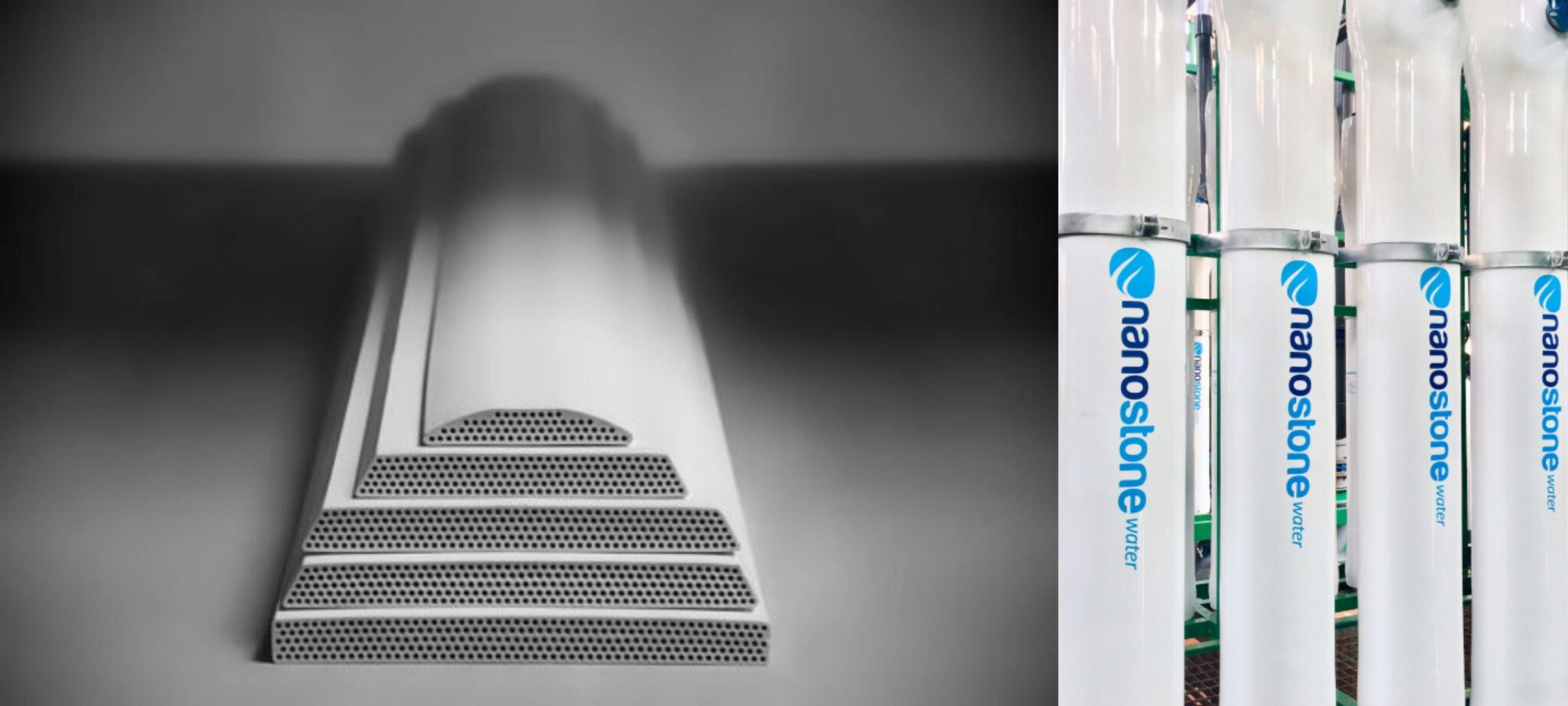

By incorporating advanced technologies like Nanostone ceramic membranes, municipalities and industries can not only meet regulatory standards but also safeguard public health, protect valuable infrastructure, and maintain operational reliability. These innovations pave the way for a future where water treatment is not only more effective but also more adaptable to the increasing challenges posed by climate change and growing industrial needs. Embracing such solutions will be key to achieving a more sustainable and resilient water future for all.